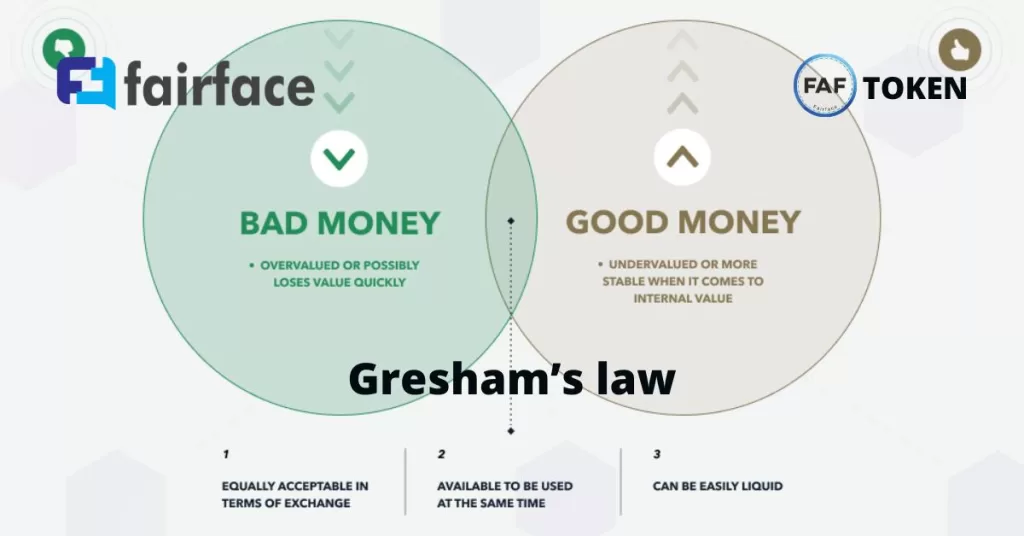
Gresham’s law is an economic principle that states that “bad money drives out good money.” It was originally formulated by Sir Thomas Gresham, an English financier, in the 16th century. The law is based on the observation that when two currencies of equal legal tender are circulating simultaneously, the currency that is less desirable—the “bad money”—will tend to drive out the more desirable currency—the “good money.”
This is because people will hoard or exchange the good money for the bad money, which they can then use to purchase goods and services. As a result, the bad money will eventually become the dominant currency in circulation.
Gresham’s law has been applied to a variety of economic situations, including the debasement of currency, the use of counterfeit money, and the rise of digital currencies.
In the context of cryptocurrencies, Gresham’s law can be seen in the way that more volatile cryptocurrencies tend to be used for speculative investments, while more stable cryptocurrencies are used for everyday transactions. This is because investors are more likely to hold onto cryptocurrencies that they believe are less likely to lose value.
Gresham’s law can also be seen in the way that some businesses are reluctant to accept cryptocurrencies as payment. This is because businesses are concerned about the volatility of cryptocurrencies and the risk that they could lose value before they can be exchanged for fiat currency.
As the cryptocurrency market continues to mature, it is possible that Gresham’s law will become less relevant. However, it is still an important principle to be aware of, as it can help to explain some of the dynamics of the cryptocurrency market.
Here are some specific examples of how Gresham’s law has been applied to cryptocurrencies:
- In 2017, during the initial coin offering (ICO) boom, many investors flocked to invest in new and untested cryptocurrencies. This led to a situation where there was an oversupply of bad money (volatile and illiquid cryptocurrencies) and a shortage of good money (stable and liquid cryptocurrencies). As a result, the prices of many cryptocurrencies crashed, and many investors lost money.
- In 2018, the cryptocurrency market experienced a significant downturn. This led to a situation where some businesses became more hesitant to accept cryptocurrencies as payment. This is because businesses were concerned about the risk that the value of the cryptocurrencies they accepted would fall before they could be converted into fiat currency.
- In 2019, there was a rise in the popularity of stablecoins. Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies that are pegged to a fiat currency, such as the US dollar. This makes them more stable than other cryptocurrencies and less likely to lose value. As a result, stablecoins have become increasingly popular as a medium of exchange and a store of value.
These are just a few examples of how Gresham’s law has been applied to cryptocurrencies. As the cryptocurrency market continues to evolve, it is likely that Gresham’s law will continue to play a role in shaping the dynamics of the market.